Cerebro spinal fluid (CSF)
Cerebrospinal fluid or CSF
CSF is the modified colour less tissue fluid. CSF present in ventricular system of brain and sub arachnoid space around spinal cord and brain.Formation
Maximum part of CSF is formed by choroid plexus of lateral ventricle, and lesser part of CSF is formed by third and fourth ventricles. Some part of CSF is also formed by capillaries present surface of spinal cord.Quantity : 150 ml
Rate of formation : 0.3ml / min
Reaction : Alkaline
Specific gravity : 1.005
Coagulation : It does not coagulate in standing
Pressure exerted in man by CSF, varies in different position...
- Lateral recumbent position : 10 - 18 cm of water
- Lying position : 13 cm of water
- Sitting position : 30 cm of water
Composition of CSF
1. Water - 99.13 %
2. Solids - 0.87%
A. Organic substances
- Proteins : 20-30 mg / dl
- Amino acids : 10 -30 mg / dl
- Sugar : 50 - 80 mg / dl
- Cholesterol : 0.06 - 0.22 mg /dl
- Urea : 10 - 30 mg / dl
- Uric acid : 0.5 - 2.2 mg / dl
- Creatinine : 0.5 - 2.2 mg / dl
- Lactic acid : 8.27 mg / dl
B. Inorganic substances
- Sodium : 350 mg / dl
- Calcium
- Potassium : 12 mg / dl
- Magnesium : 3 - 3.6 mg / dl
- Chlorides : 700 - 750 mg / dl
- Phosphate : 1.8 mg / dl
- Bicarbonates : 40 - 60 mg / dl
- Sulfates : 0.6 mg / dl
 |
| Composition of CSF |
Absorption of CSF
- It absorbed mainly through arachnoid villi and it drain into cranial venous sinuses.
- It also absorbed by lymphatic present around 2nd, 7th and 8th cranial nerves.
- It also absorbed by veins around spinal nerves.
Circulation
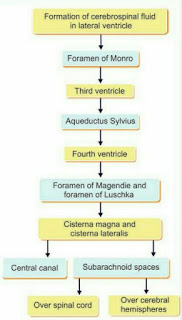
- CSF passes from lateral ventricles to third ventricle by the inter ventricular foramen or foramen of monro.
- It passes from third to fourth ventricle by the Aqueductus Sylvius.
- It enters from fourth ventricle to cisterna magna and cisterna lateralis through foramen of magendie ( central opening ) and foramen of luschka ( lateral opening ).
- From cisterna magna and cisterna lateralis, CSF circulates through subarachnoid space and cerebral hemispheres. It flows also into the central canal of spinal cord.
 |
| Circulation of CSF |
Functions
- Protection
- Nutrition
- Excretion
Applied physiology
1. For diagnosis of disease, bio-chemical examination of CSF.
2. Any obstruction to flow of CSF in ventricle it causes...
- Increase intra cranial pressure in adults.
- Hydrocephalus in children's.
3. CSF is obtained by...
- Lumbar puncture - between 3rd and 4th lumbar spine.
- Cisternal puncture.
- Ventricular puncture.
Images copied from Physiology Sembulingum book






Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box