Name :- Golgi apparatus, Golgi body, Golgi complex, Post office of the cell, Shipping department of the cell (Camillo Golgi (1898) first discovered, hence the name is Golgi).
Properties :
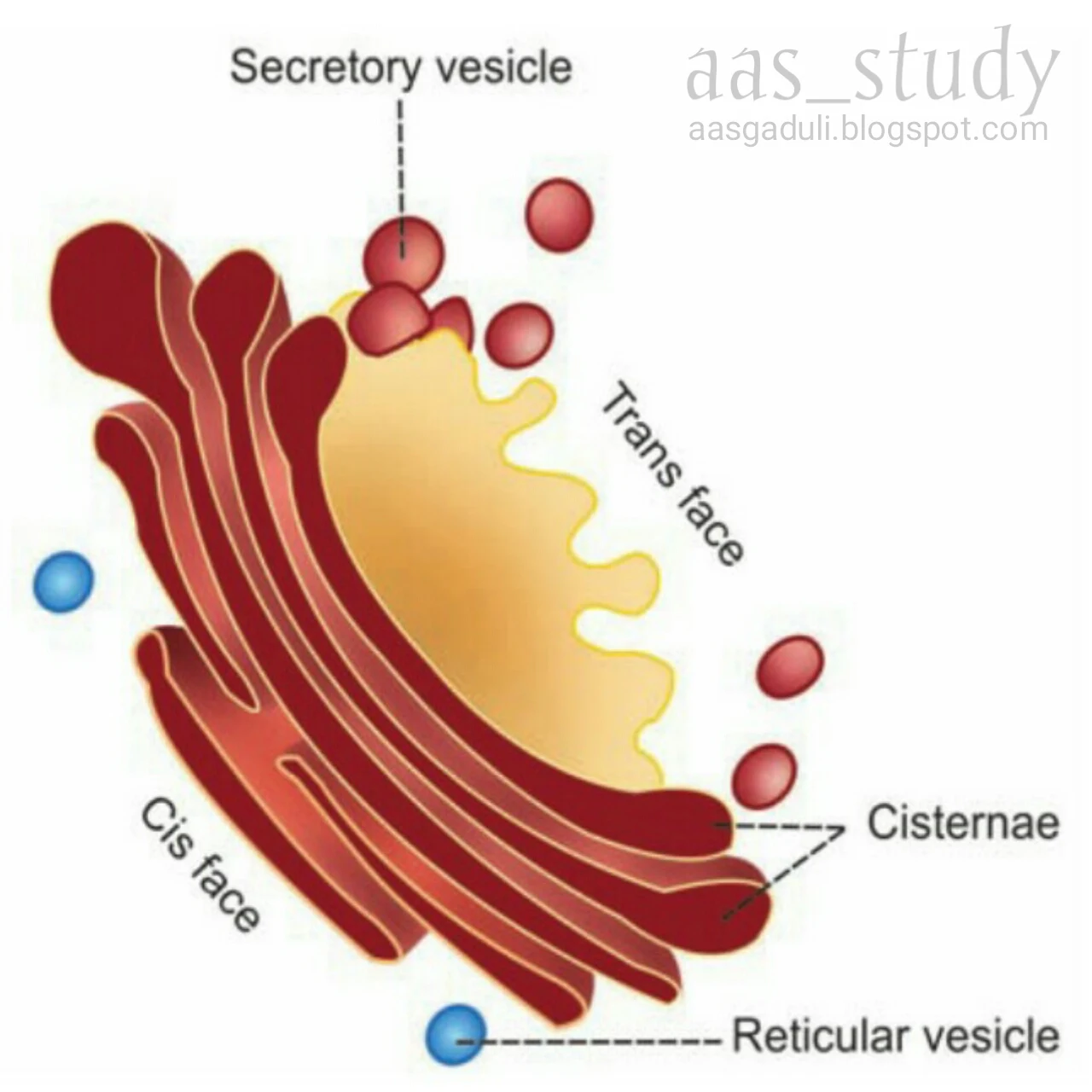
- It is an membrane bound organelle situated near the nucleus.
- It is present in all cells except RBCs.
- Usually, each cell has one Golgi apparatus.
- Each Golgi apparatus consists of 5-8 flattened membranous sacs called cisternae (0.5-1.0 micrometer).
- Golgi apparatus has two ends or faces, namely cis face (situated near the endoplasmic reticulum) and trans face (situated near the cell membrane).
Functions :
Major functions of Golgi apparatus are processing, packing, labeling and delivery of proteins and lipids to different part of the cell or outside of the cell.
- Processing :- glycoproteins and lipids are modified here.
- Packaging :- modified materials are packed in the form of secretory granules, secretory vesicles and lysosomes.
- Labeling and delivery :- Golgi apparatus sort out the processed materials and labels them (such as phosphate group) then distribute in or out side of the cell according to demand.
Similar Posts :-






No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box