Femur
- The femur is a latin word it means thigh.
- Femur is the longest and strongest bone of the body.
- Femur has 27% length of total body length.
- Weight of femur is about 380gm in males and 279gm in females.
- Quantity of femur are two in number.
Side Determination
1. Head directed medially.
2. Medial and lateral condyle (lower end) inferiorly.
3. Cylindrical shaft is convex forward.
Joint Formation
1. Hip joint - between head of femur and acetabulum of Hip bone.
2. Knee joint - between lower end of femur and upper end of Tibia.
Features
Upper end
- It has head, neck, greater trochanter ( Greek- runner), lesser trochanter, intertrochantric line and intertrochantric crest.
Head -
- It forms more than half a sphere and is directed madially, upwards and slightly forwards.
- It articulates with the acetabulum to form hip joint.
- It has a pit that is called fovea.
Neck -
- It is about 3.7cm long.
- It connects the head with the shaft.
- It has two border ( upper,lower) and two surfaces ( anterior, posterior).
- It meet the shaft at the intertrochantric crest.
- The neck makes the angle with the shaft called Neck-shaft angle which is about 125⁰, it is less in female due to their wider pelvis.
- Trochanter-shaft angle is about 8⁰ in adults.
- The angle of femoral torsion or angle of anteversion it forms between transverse axes of the upper and lower end, which is about 15⁰.
- Blood supply of the neck through retinacular arteries and medial circumflex of femoral arteries.
Greater Trochanter -
- It is large quadrangular prominence located at the upper part of the junction of the neck with the shaft.
- It has an upper border with an apex, and three surfaces (anterior, Medial and Lateral).
- Medial surface has fossa called trochantric fossa.
Lesser Trochanter -
- It is a conical eminence directed medially and backwards from the junction of the posteroinferior part of the neck with the shaft.
Intertrochanteric line -
- It marks the junction of the anterior surface of the neck with the shaft.
Intertrochanteric crest -
- It marks the junction of the posterior surface of the neck with the shaft.
 |
| Right femur Posterior aspect |
Shaft
- The shaft is more or less cylindrical.
- It is narrowest in middle, and is more expanded inferiorly than superiorly.
- It is convex forward.
- In the middle one-third, the shaft has three borders ( Medial, Lateral and posterior ) and three surfaces ( anterior, Medial and Lateral).
- Posterior border has a roughned ridge called linea aspera (latin- rough line).
- In the upper one-third of the shaft, the two lips of the linea aspera diverge to enclose an additional posterior surface
- Thus this part has...Four borders ( Medial, Lateral, Spiral line and The lateral lip of the gluteal tuberosity), Four surfaces ( Anterior, Medial, Lateral, Posterior).
- In the lower one-third of the shaft, the two lips of the linea aspera diverge as supracondylar lines to enclose the additional , popliteal surface
- Thus this part has... Four borders ( Medial, Lateral, Medial supracondylar line and Lateral supra condylar line), Four surfaces ( Anterior, Medial, Lateral and Popliteal).
Lower end
- The lower end of the femur is widely expanded to form two large condyle (Medial and Lateral).
- Anteriorly the two condyle united are in line with the front of the shaft.
- Posteriorly these condyle are separated by a deep gap called Intercondylar fossa or intercondylar notch.
Articular surface -
- The articular surface for Patella covers by the anterior surface of both condyle.
- The articular surface for Tibia covers by the inferior and posterior surface of both condyle.
Lateral condyle -
- The lateral condyle is flat laterally, and is more in line with the shaft.
- Tough it is less prominent than the medial condyle, it is stouter and stronger.
Lateral aspect has...
- a. A prominence called the Lateral Epicondyle.
- b. Popliteal Groove which lies just below the epicondyle. It has deeper anterior part and shallower posterior part.
- c. A Muscular Impression posterosuperior to the epicondyle.
Medial Condyle
- The condyle is convex medially.
- The most prominent point on it called Medial Epicondyle.
- It has a projection called Adductor Tubercle which is located posterosuperior to the epicondyle. This tubercle is an important landmark, epiphyseal line for the lower end of the femur passes through it.
Intercondylar Fossa or Intercondylar notch
- This notch separates the and posterior parts of the two condyles.
- It is limited anteriorly by the patellar articular surface, and posteriorly by the intercondylar line which separates the notch from the popliteal surface.
Attachment on the femur
 |
| Attachment on the anterior aspect (Right femur |
Fovea on the head of femur
It provide attachment to the Ligament of the head of femur / Round ligament / Ligamentum teres / Ligamentum femoris.
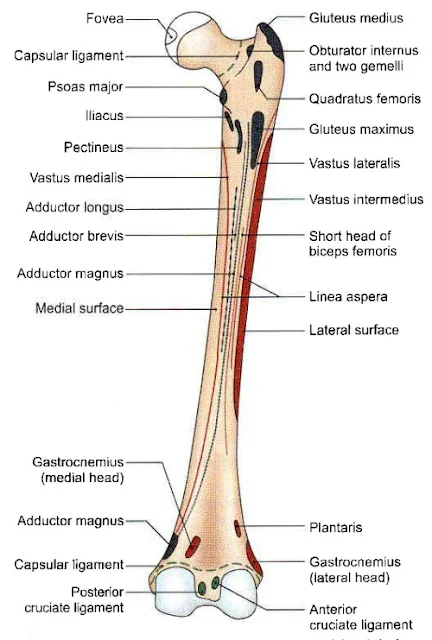 |
| Attachment on the Posterior aspect (Right femur ) |
Greater trochanter
Insertion - Piriformis, Gluteus minimus, Obturator internus, Two gemelli, Obturator externus and Gluteus medius.
The trochantric bursa of gluteus maximus lies behind the ridge.
 |
| Upper end of the right femur (a) Medial aspect (b) Lateral aspect |
Lessor trochantor
Insertion - Psoas major and Iliacus.
Lesser trochantor is covered by a bursa that lies deep to the upper horizontal fibres of the adductor magnus.
Intertrochanteric line
Attached - capsular ligament ,iliofemoral ligament.
Origin - vastus lateralis.
Quadrate tubercle
Quadratus femoris insert on it.
Shaft
Origin - Gastrocnemius, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, articularis grnu,
short head of biceps femoris, plantaris.
Insertion - Gluteus maximus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, pectineus intermuscular septa.
Lateral condyle
Fibulo co-lateral ligament are attach on it.Origin - Popliteus, lateral head of the gastrocnemius.
Medial condyle
Tibial co-lateral ligament attach on it.
Insertion - Hamstring or ischial head of the adductor magnus.
Intercondylar notch
Attached - Anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, capsular ligament (intercondylar line), infrapatellar synovial fold.
Nutrient artery to the Femur
- Nutrient artery derived from the second perforating artery, branch of profunda femoris artery.
- The nutrient foramen is located on the medial side of the linea aspera.
Ossification
- Femur ossifies from one primary (for shaft ) and four secondary centre (one for lesser trochanter, one for greater trochanter, one for head and one for lower end).
 |
| Ossification of femur |
Applied
- Fracture of the shaft.
- Fracture of the neck of femur.























