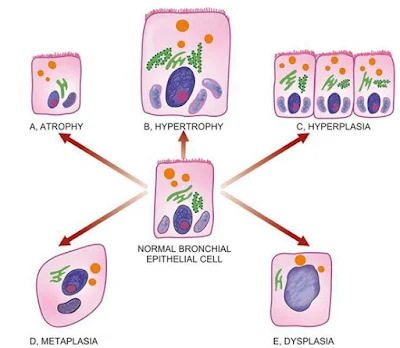
Definition –
Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of parenchymal cells resulting in
enlargement of the organ or tissue. Quite often, both hyperplasia and
hypertrophy occur together.
Causes –
It may be physiological or pathological…
PHYSIOLOGICAL
HYPERPLASIA –
1. Hormonal hyperplasia, it
occurs due hormonal stimulation.
a.
Hyperplasia of female
breast at puberty, during pregnancy and lactation.
b.
Hyperplasia of pregnant uterus.
c.
Proliferative activity of
normal endometrium after a normal menstrual cycle.
d.
Prostatic hyperplasia in
old age.
2. Compensatory hyperplasia
i.e. it occurs due to removal of part of an organ or in the contralateral organ
in paired organ e.g.
a.
Regeneration of liver after
partial hepatectomy.
b.
Regeneration of epidermis
after skin abrasion.
c.
Hyperplasia of nephrons
after another nephrectomy.
PATHOLOGICAL
HYPERPLASIA – It is occurs due to excessive stimulation of hormones or growth
factors e.g.
- Endometrial hyperplasia due to excess oestrogen.
- In wound healing, there is formation of granulation tissue due to proliferation of fibroblasts and endothelial cells.
- Formation of skin warts from hyperplasia of epidermis due to human papilloma virus.
- Pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia of the skin occurring at the margin of a non-healing ulcer.
- Intraductal epithelial hyperplasia in fibrocystic change in the breast.
MORPHOLOGICAL
FEATURES –There is enlargement of the affected organ or tissue and increase in
the number of cells due to increase DNA synthesis resulting in increase mitoses
of the cells.
“Hyperplasia occurs in labile cells (epithelial cells of the skin,
mucous membrane, lymph nodes, cells of bone marrow), stable cells (parenchymal
cells of the liver, kidney, pancreas, adrenal, thyroid) while hyperplasia does
not occurs in permanent cells (neurons, cardiac and skeletal muscles)”
 |
| Adaptive Disorders |
Similar Posts -






No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box