Superior vena cava
- Superior vena cava is a large venous channel which collects blood from the upper half of the body and drain into the right atrium.
- Superior vena cava is about 7cm long.
- It is formed by the union of the right and left brachiocephalic or innominate veins.
- It begins behind the lower border of the first right costal cartilage close to the sternum.
- It terminates by the opening into the upper part of the right atrium behind the third right costal cartilage.
- It has no valves.
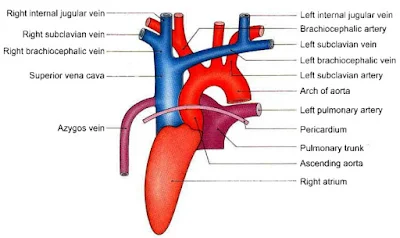 |
| Superior vena cava and it's relations |
Relations
Anterior
- Chest wall.
- Internal thoracic vessels.
- Anterior margin of the right lung and pleura.
- The vessel is covered by pericardium in its lower half.
Posterior
- Trachea
- Right vagus
- Root of the right lung
Medial
- Ascending aorta
- Brachiocephalic artery
Lateral
- Right phrenic nerve and vessels
- Right pleura and lung
Tributaries of the superior vena cava
- Azygos vein ( at the level of second costal cartilage ).
- Several small mediastinal and pericardial veins drain into the vena cava.
Applied anatomy
- Obstruction of superior vena cava above the opening of the azygos vein.
- Obstruction of the superior vena cava below the opening of the azygos vein.
- Obstruction of the superior vena cava is indicates the mediastinal syndrome.
Image copied from BD Chourasia book






No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box